Mitosis
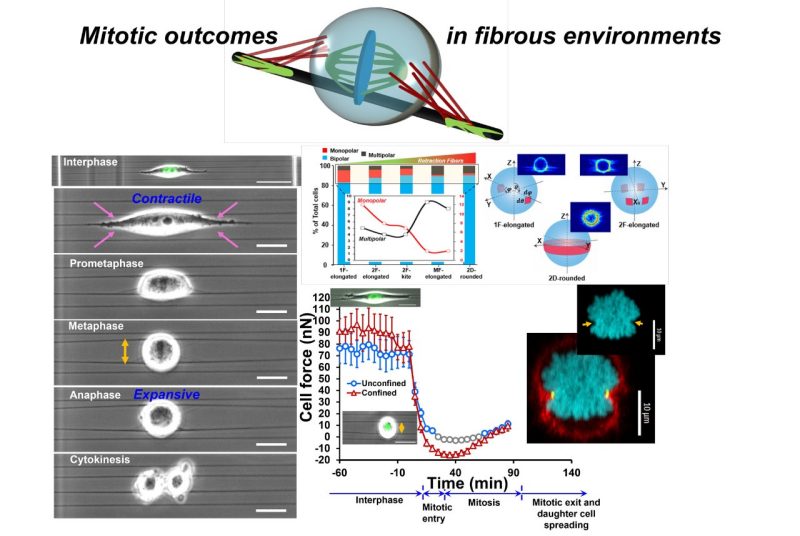
During mitosis, cells round up and generate outward forces to create space and orient the mitotic spindles. Here, using suspended ECM-mimicking nanofiber networks, we recapitulate in vivo adhesion organization and confinement to interrogate mitotic outcomes for various interphase cell shapes. Elongated cells attached to single fibers through two focal adhesion clusters (FACs) at their extremities result in perfect spherical mitotic cell bodies that undergo large 3D displacement while being held by retraction fibers. Increasing the number of parallel fibers increases FACs and retraction fiber-driven stability, leading to reduced 3D cell-body movement, metaphase plate rotations, and significantly faster division times. Interestingly, interphase kite shapes on a crosshatch pattern of four fibers undergo mitosis resembling single-fiber outcomes due to rounded bodies being primarily held in position by retraction fibers from two perpendicular suspended fibers. We develop a cortex-astral microtubule analytical friction and force model to capture retraction-fiber-driven stability of the metaphase plate rotations. We report that reduced orientational stability results in increased monopolar mitotic defects. Our theoretical and computational framework explains the core switch in mitotic error with increasing retraction fiber stability. In the case of cells attached to two parallel fibers, rounded mitotic cells can get confined between the suspended fibers, allowing estimation of the mitotic forces through measurement of the outward deflection of the fibers. Interestingly, confinement causes rotated mitotic spindles similar to those reported in dense tissues. Overall, we establish mitotic outcomes in fibrous environments governing interphase cell shapes, adhesion geometries, and varying levels of mechanical confinement.
Collaboration with: Prof. Jake DeLuca, Prof. Nir Gov, Prof. Raja Paul


